Premature ejaculation (PE) is a common sexual health concern that affects a significant number of men worldwide. It refers to a condition where a man ejaculates earlier than desired during sexual activity, often leading to distress and dissatisfaction for both partners. This blog aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of premature ejaculation, including its causes, treatment options, and management techniques.
I. What is Premature Ejaculation?
Premature ejaculation is a condition occured in men when semen is released from the penis earlier than desired during sexual activity. It Happens with minimal sexual stimulation and before the person desires. It can happen during vaginal intercourse or other forms of sexual activity. While there is no specific time limit to define premature ejaculation, it is generally considered if it occurs within one minute of penetration.
Frustration and anxiety may arise as a consequence of premature ejaculation. In certain cases, people experiencing this condition may have a lower frequency of sexual activity than desired or choose to avoid it altogether. However, there are available treatments that can provide assistance.
II. Causes of Premature Ejaculation or quick release of sperm
Premature ejaculation, or quick release of sperm, can have various causes, including:
- Psychological or emotional Factors: Performance anxiety, stress, depression, guilt, relationship issues, Lack of confidence or poor body image, Negative feelings about the idea of sex or past traumatic experiences can contribute to premature ejaculation.
- Biological Factors: Hormonal imbalances, abnormal levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, genetic predisposition, inflammation or infection of the prostate or urethra, or certain medical conditions can play a role.
- Early Sexual Experiences: Negative or hurried early sexual experiences can lead to conditioned responses that contribute to premature ejaculation later in life.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Men who experience difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection may develop a pattern of rapid ejaculation to compensate for the erectile issue.
- Lifestyle and Habits: Excessive alcohol consumption, substance abuse, smoking, and poor overall health can contribute to premature ejaculation.
III. Treatment/Cure or Self Cure Options for Premature Ejaculations:
Curing premature ejaculation involves a multifaceted approach. Here are some strategies that can help:
- Behavioral Techniques:
-
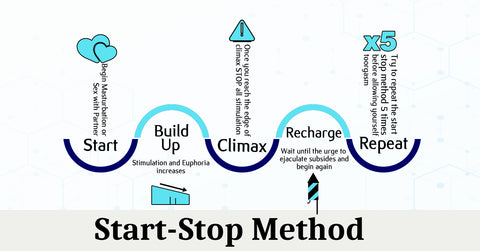
Start-stop method: This involves stopping sexual stimulation before reaching the point of ejaculation and then resuming after a brief pause.
- Squeeze technique: The base of the penis is gently squeezed to decrease arousal and delay ejaculation.
- Masturbating before sex: This can help some men prolong their sexual performance during intercourse.
-
Strengthen your muscles: To enhance muscle strength, focus on your pelvic floor muscles as they can play a role in premature ejaculation. Consider practicing Kegel exercises to strengthen them. Identify the relevant muscles by pausing the flow of urine midstream. Contract and hold them tightly for 3 seconds, then release for 3 seconds. Aim to repeat this exercise at least three times a day, completing 10 repetitions each time.
Note: Start-stop method & squeeze method are most trust methods is recommended by urology care foundation. - Medications:
- Topical creams or long time sprays: These numbing agents are applied to the penis to reduce sensitivity and delay ejaculation.
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): Certain antidepressants like fluoxetine and sertraline have been found to help delay ejaculation. However, they should only be used under medical supervision.
- Counseling:
- Couples therapy: Involving both partners can address relationship issues and improve communication and intimacy.
- Individual therapy: Psychotherapy can help identify and address psychological factors contributing to premature ejaculation.
- Counseling or Therapy:
- Seeking the guidance of a sex therapist or counselor can be beneficial, particularly when psychological factors contribute to premature ejaculation.
IV. Management Techniques:
- Pelvic floor exercises: Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles through exercises like Kegels can improve control over ejaculation.
- Sexual techniques: Experimenting with different sexual positions and pacing can help prolong sexual activity and delay ejaculation.
- Open communication: Talking openly with your partner about expectations, desires, and concerns can reduce anxiety and enhance intimacy.
V. When to Seek Professional Help:
If premature ejaculation becomes a persistent problem and significantly affects your sex life and overall well-being, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional like PositiveGems' Expert Team. They can provide a proper diagnosis, identify underlying causes, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Conclusion:
Premature ejaculation can be a challenging condition to manage, but with the right strategies and support, it is often possible to improve sexual satisfaction and performance. By understanding the causes, exploring treatment options, and implementing effective management strategies, individuals and their partners can work towards a fulfilling and enjoyable sexual relationship.
Note: The information provided in this blog post is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment options based on your individual circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: Is Premature Ejaculation normal or not?
A: Premature ejaculation is a normal sexual problem in people. if it happens occasasionly. However, if it happens consistently and causes distress or interferes with sexual satisfaction, seeking medical advice is recommended. Note:
While it can be frustrating and even embarrassing, premature ejaculation is a normal problem in men. Approximately 20% to 30% of men experience it at some point in their lives.
As stated by the American Urological Association, premature ejaculation is the most prevalent form of sexual dysfunction in men. Approximately one out of every five men, aged 18 to 59, report experiencing instances of premature ejaculation.
Q: Can premature ejaculation happen at any age?
A: Yes, premature ejaculation can happen at any age. It is not limited to a specific age group and can affect men in their teens, twenties, thirties, or older. It is important to note that seeking medical advice and exploring treatment options is recommended regardless of age.
Q: Is premature ejaculation normal or not?
A: Premature ejaculation is a common sexual concern experienced by many individuals. It is considered normal if it occurs infrequently. However, if it happens consistently and causes distress or interferes with sexual satisfaction, seeking medical advice is recommended.
Q: Is it normal to last 3 minutes in bed?
A: The duration of sexual intercourse can vary among individuals, and what is considered normal can vary as well. While there is no strict definition of what is considered a "normal" duration.
However, the survery of Society for Sex Therapy and Research member survey 2005, Vaginal Sex lasts 3-5 minutes is considered as Normal. While, 1-2 minutes is “too short.” and 10 to 30 minutes is considered “too long.
Q: Can I prevent premature ejaculation?
A: Yes, you can prevent premature ejaculation by yourself. By abovementioned techniques i.e. start-stop method or the squeeze technique, Masturbating before sex, and Kegel exercises to strengthen your muscles. Open communication with your partner, managing stress and anxiety, and incorporating relaxation techniques can also be beneficial.
Q: Can wearing a condom help with premature ejaculation?
A: Yes, by applying a condom on your penis can reduce sensitivity, potentially aiding in the delay of ejaculation.
Q: Is premature ejaculation harmful?
A: No, Premature ejaculation is generally not considered harmful in a physical sense. However, it can be a source of emotional distress and may impact sexual satisfaction and relationships.
Q: What’s the difference between erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation?
A: Erectile dysfunction (ED) and premature ejaculation (PE) are different sexual conditions. ED refers to the inability to achieve or maintain an erection, while PE is ejaculating too quickly. ED is related to difficulties with the physiological aspect of achieving and sustaining an erection, whereas PE focuses on the timing of ejaculation. While they can occur separately, it is also possible for an individual to experience both conditions simultaneously.
Q: Can drinking alcohol help to reduce premature ejaculation?
A: Alcohol can affect your ability to perceive sexual stimulation by disrupting the communication between your brain and genitals. This interference can result in difficulties ejaculating (reaching orgasm) or experiencing premature ejaculation (ejaculating too quickly). Heavy alcohol consumption may lead to these sexual performance issues, so it is advisable to moderate alcohol intake or use Long Time Delay Spray by PositiveGems for a healthier sexual experience.
Q: What are the Symptoms of premature ejaculation?
A: Symptoms of premature ejaculation include consistently ejaculating within a minute of sexual activity, experiencing difficulty delaying ejaculation during intercourse, feeling distressed or frustrated about the inability to control ejaculation timing, and avoiding sexual intimacy due to concerns about ejaculating too quickly.
Still have Questions?
Please Call our Customer Success Team